Today chess is a game known as a benchmark for intelligence worldwide. But that’s not how our ancestors looked at it. Representation of power, a poetic metaphor, and even a part of traditions were the few roles chess played in the past. The game of chess evolved throughout centuries and gave birth to games like shogi and Xiangqi in the process. The history of chess is nothing but iconic, how it survived and evolved into the game that we all love so much today!
Table of Contents
ToggleOrigin and Propagation
The First Chess - Chaturanga 6th Century
Today we can trace chess early reminisces way back to 6th century India. At least 1500 years ago, a great warrior prince of the Gupta dynasty (India) died on the battlefield. His brother devised an 8×8 board and pieces representing the King, chariot, and elephants to give her mother insight into what happened on the battlefield.
Pieces were given movement restrictions according to their battle calibers on the battlefield. An elephant was more free to move than a chariot but restrained to directions. The game was known as Chaturanga then, a Sanskrit word representing things with four parts. The 8×8 board is divided into four big squares, with every court having its players.
The game of Chaturanga gains an upper hand over the games like chausar (ancient Indian ludo) and other games based purely on luck and spread throughout the dynasty.


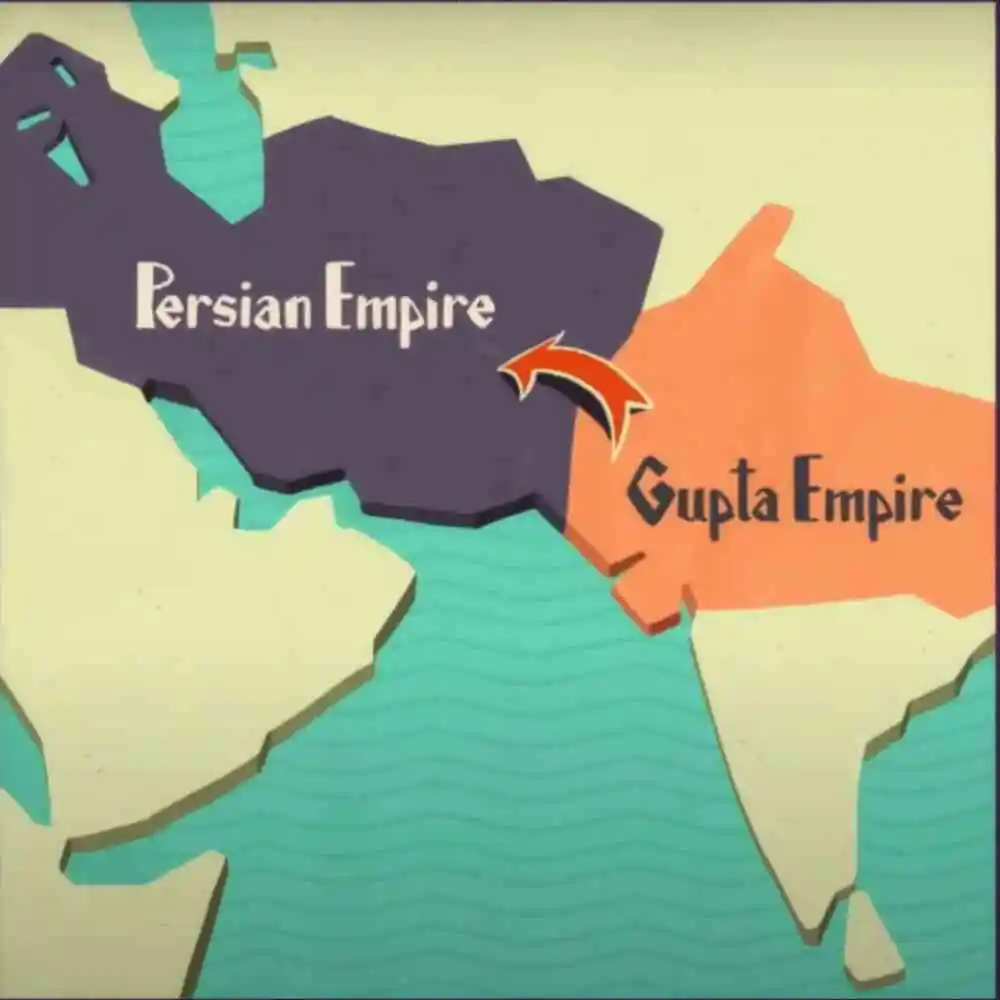
Persian chess - Shatranj 8th century
Chaturanga then spread along the neighboring emperors and was adopted by Persians. Exposure to new territories comes with further modifications. Several rules have changed as well as the pieces. The resulting game is quite similar to modern chess named Shatranj.
Shatranj is the Persian for King under threat. The principle of checkmate was also derived in this era known as Shahmat at that time. After the conquest of Persia, the game was introduced to the Muslim world (Islamic Countries) which further led to the game spreading in Asia.
Reroute to East Asia - 10th century
India and China were the trading hubs back then. Traders from all over the world travel to these countries to sell their goods. You might have heard the terms silk route and Mohenjo-Daro; they were nothing but the biggest trading route and trading cities. Traders carry culture along with them as well as chess.
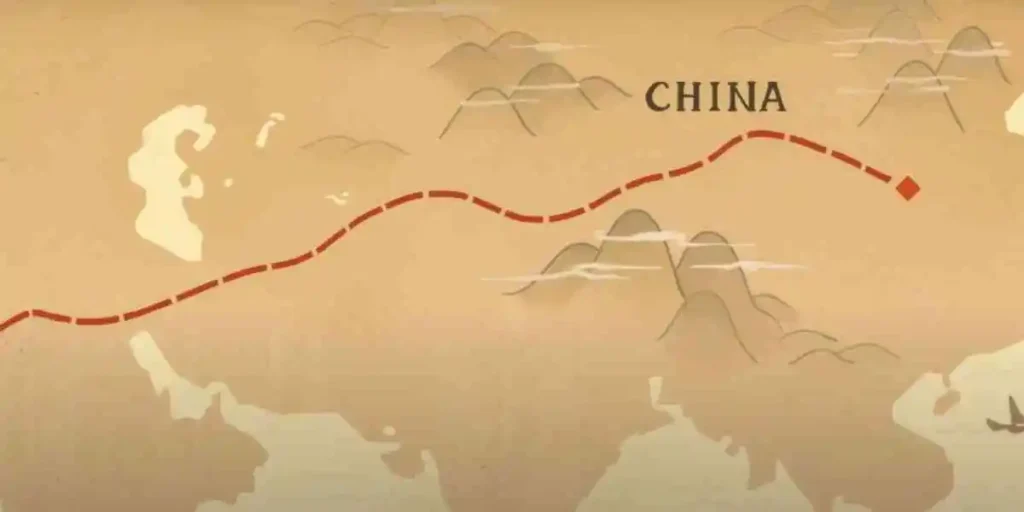
Shatranj makes its way to the Chinese territories from the silk route. New variants were devised from shatranj, and some of them are played to the present. Pieces were placed at the intersection of lines instead of the box itself, an opponent can capture and reuse the pieces for themselves, and fixed defenses were some of the modifications that china added to the history of chess.


History of Shogi - Japan
Shogi is a chess variant known for its three-dimensional modifications to the game. The origins of shogi were found in ancient Japan. The game traveled from India to China and finally arrived in Japan. Shogi is a well know game played internationally now and among the chess varieties that were popular in the past.
European chess till the late 17th century
Versus de scachis a poem on chess, the first ever mention of chess in text or literature, written in early Europe. Europeans were fascinated by the game of chess. Chess strategies and theories were born in Europe in the burning heat of evaluation. To make the game of chess entertaining and fast to play rules were introduced like:-
- Pawns can now move two ranks on the first move – late 13th century
- The en passant rule is introduced – in the late 14th century

- A strong queen replaces the Minister or adviser.
- Castling and the modern moves for the queen and bishop were slowly adopted.
Pieces were given human faces and became representatives of the different classes of society. Interestingly, chess was also adopted as a subject in the student curriculum, but the churches remained suspicious of chess and enforced laws to detain the game. Foldable chess was one of the brilliant inventions born of the desire to play. The folded chess board appears as a book, and citizens can carry it without restriction.
Chess players start analyzing the game and innovating new ways to gain an advantage from the beginning. In accordance with that, Repeticion de Amores y Arte de Ajedrez by the Spaniard Luis Ramirez de Lucena, published in 1497, was the first book that includes an analysis of eleven chess openings. There on, the era of Modern chess began!
Fun Facts
- A rookie, or a player with no experience, is named after a rook in chess.
A rook is generally the last piece to be moved into action, as well as a rookie. - It was about chess that the second English book of all time was printed!
- 100 moves without capture were made during the match between Thorton and Walker in 1992

Modern Chess
The era of modern chess began with the London chess tournament in 1851. The first chess tournament ever played. Adolf Anderssen, the organizer of the event, was a german grandmaster known for games like Immortal Game in 1851 and Evergreen Game in 1852. He won the tournament in 1851 but lost in the consecutive year to another player.

Chess was unrefined back then, with no time barrier, players even took days to play their moves, extending tournament duration to months. In 1861 a sand clock was used as a time barrier for players to accelerate gameplay. The Analog chess clock was the by-product of further modifications. Thomas Bright Wilson and Joseph Henry Blackburne came up with the idea of the analog clock and used it for the first time in the London tournament in 1883.
Chess before FIDE
Fédération Internationale des Échecs (FIDE) is an organization established on July 20, 1924, in Paris, France is the regulatory body for international chess. More than 200 countries are members of FIDE, and it is the organizer of all international tournaments. Before FIDE, tournaments were organized privately by anyone who sought to be the world champion. The strongest player claims their rightfulness for the title, and whoever wins is declared the world champion.
In 1886, the first world title match was held between With Steinitz and Zukertort, two of the best players in the world. Steinitz won and became the first world champion. Players began to analyze the games that gave birth to many lines and variations. The world title them passed on to many great players of various countries until world war 2 when the USSR’s domination began.

Rise of USSR
After the second world war, FIDE became the official organization, and top players across the globe had to compete against each other in candidate tournaments to challenge a champion. Alexander Alekhine, the last world champion before FIDE began to organize world championships, died in 1946 while still holding the title of World champion. To decide the new World champion FIDE organized the first world championship in 1948.
Mikhail Botvinnik from USSR became world champion by defeating the runner-up Vasily Smyslov again from USSR. From there on, USSR dominated the game of chess by producing more than ten world champions in half a decade. Bobby Fisher was the only player who managed to take over the World champion title from USSR from 1948 to 1999. Viswanathan Anand an Indian grandmaster put an end to the USSR streek and become world champion in 2000.
History of Chess Olympiad
Chess Olympiad is a country representative match in which teams from various countries compete against each other. The history of the chess olympiad goes way to the 1924 Olympics when the first attempt to integrate the game of chess into the Olympics failed.
In pursuit of the same, FIDE organized the event of the chess Olympiad in 1927 in London. The chess Olympiad takes place every two years, from then on except in 1950 due to World War 2. Chess Olyampiad 2019-20 was the first virtual chess Olyampiad event played in the histroy of chess due to the unforseen events of covid – 19.

AI and Super Computers
In the twenty-first century, we also began to serge the idea of utilizing machine learning in the game of chess. We all heard the stories of the Mechanical Turk that played chess and defeated many great players like Napoleon Bonaparte in the past, but what if that cheap trick was real? With that idea, engineers began to work on chess learning AIs and supercomputers.
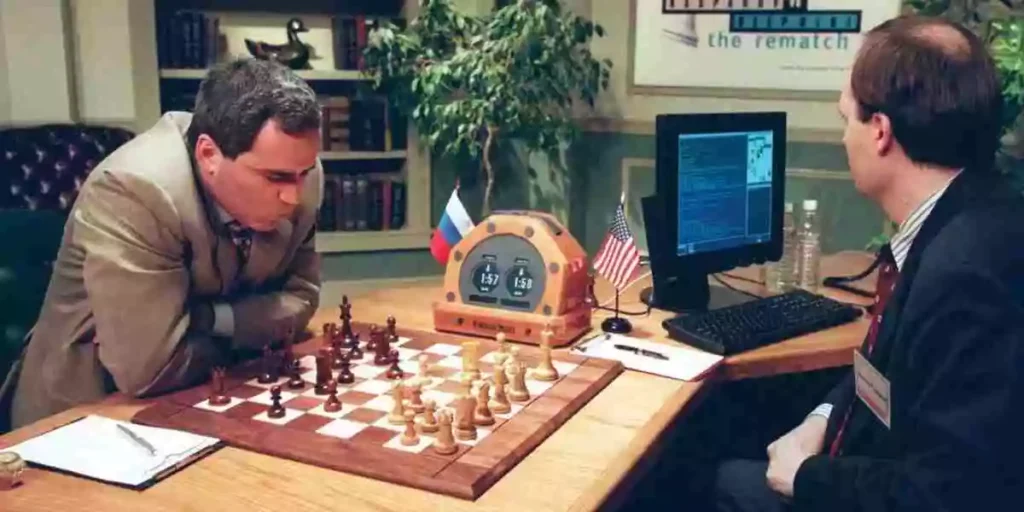

On May 11, 1997, a supercomputer made by IBM, Deep Blue, defeated the human world champion, Garry Kasparov. Supercomputers surpassed human intelligence in the game of chess and defeated many world champions since then.
Today the game of chess is one the most played board games with over 800 million players. Every year we witness many new players emerging and setting up new records. What we just read was once present, and sooner than we know it, what we know will be passed. The only thing that was and will be the same is the passion for the game of chess!
- Aryan Kumarhttps://way2wise.com/author/aryan-kumar/
- Aryan Kumarhttps://way2wise.com/author/aryan-kumar/
- Aryan Kumarhttps://way2wise.com/author/aryan-kumar/
- Aryan Kumarhttps://way2wise.com/author/aryan-kumar/





